If you live in Chicagoland or any of the upper Midwest and Northeast states, you’ve seen a noticeable gloom and haze in the air. The Canadian wildfires are wreaking havoc on the air quality in numerous parts of the country. On Tuesday, June 27, 2023, Chicago reported the worst air quality in the world, according to IQAir.com, a service that tracks air quality around the globe.
While Chicago’s poor air quality is an anomaly, there is a lesson to be learned from the wildfires and the health ramifications of poor air quality.
Poor air quality can harm vulnerable populations and those with pre-existing health conditions. Before going outside, you can check the air quality in your city here.
Air Pollution Facts
According to the Environmental Defense Fund, nearly 40% of Americans live in areas with unhealthy levels of smog pollution. Many major cities are covered in a hazy brown fog known as smog. Smog results from industrial emissions from power plants, factories, manufacturing plants, cars, and other sources. It reacts with the sunlight and heat in the atmosphere, resulting in a significant air pollutant.
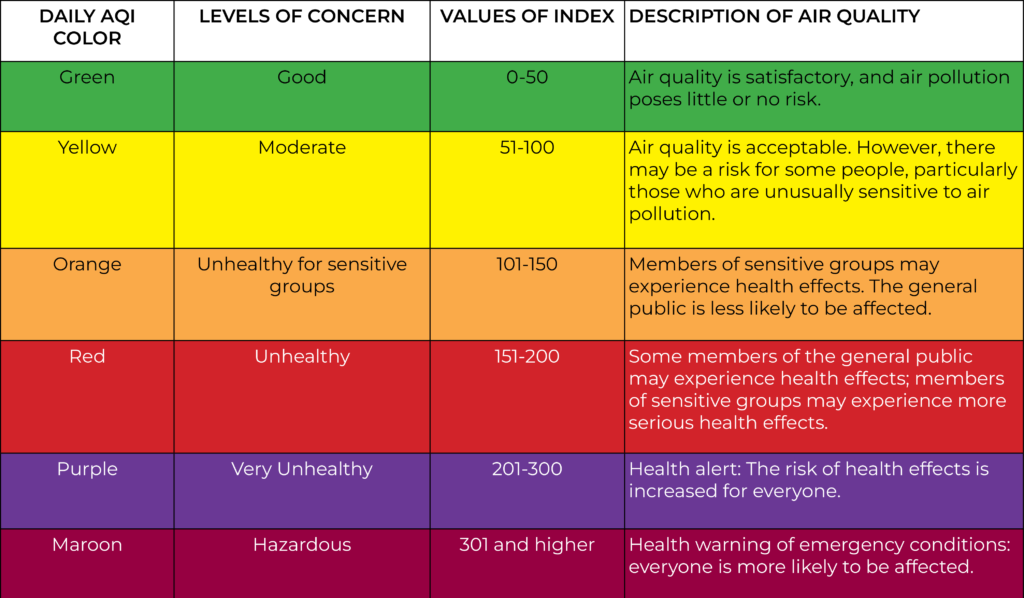
The EPA developed the U.S. Air Quality Index (AQI) to report air quality across the nation. AQI runs on a scale from 0 to 500 – the higher the number, the greater level of air pollution and the higher risk for health concerns.
The following table highlights ozone and particle pollution basics, taken from airnow.gov.
The Clean Air Act
The Clean Air Act regulates five major pollutants:
- ground-level ozone
- particle pollution (also known as particulate matter, including PM2.5 and PM10)
- carbon monoxide
- sulfur dioxide
- nitrogen dioxide
Air pollution is a concern in many large cities, and Chicago is no exception. The City Council approved the Air Quality Ordinance, which regulates the construction and expansion of certain facilities that produce and create air pollution. Certain pollutants still pose significant challenges. Here are some things to be aware of regarding Chicago air pollution:
- Ozone (O3) Pollution: Ozone is a harmful gas formed when pollutants from vehicles, industry, and other sources react in the presence of sunlight. Chicago experiences high levels of ozone pollution during the summer months due to factors such as vehicle emissions, industrial activity, and weather conditions. Ozone can irritate the respiratory system, trigger asthma attacks, and cause other respiratory symptoms.
- Particulate Matter (PM) Pollution: Particulate matter consists of tiny particles suspended in the air, and it can be categorized into two main types: PM2.5 and PM10. PM2.5 refers to particles with a diameter of 2.5 micrometers or smaller, while PM10 refers to particles with a diameter of 10 micrometers or smaller. These particles can come from various sources, such as vehicle exhaust, power plants, construction sites, and industrial emissions. Long-term exposure to PM2.5 and PM10 can have adverse health effects, including respiratory and cardiovascular problems.
- Industrial and Traffic Emissions: Chicago is a major transportation hub and home to numerous industrial facilities. These activities contribute to air pollution through emissions of pollutants such as nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulfur dioxide (SO2), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and particulate matter. The proximity of highways and heavy traffic areas can further exacerbate pollution levels in certain neighborhoods.
- Environmental Justice Concerns: Air pollution disproportionately affects disadvantaged communities in Chicago. Low-income neighborhoods and communities of color often face higher pollution levels due to factors like the location of industrial facilities and transportation corridors. This inequitable distribution of pollution can lead to increased health disparities and environmental justice concerns.

How Harmful Is Air Pollution to Your Health?
Smog is particularly harmful when inhaled. It irritates your airways, can increase the risk of serious heart and lung diseases, and can have long-term effects on the respiratory and cardiovascular systems and overall well-being.
Here are some ways air pollution can affect your health:
- Respiratory Problems: Air pollution can irritate the respiratory system, leading to coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, and exacerbating existing respiratory conditions such as asthma, bronchitis, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Long-term exposure to air pollution can also increase the risk of developing respiratory infections and lung cancer.
- Cardiovascular Issues: Inhalation of air pollutants, particularly fine particulate matter (PM2.5) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2), can penetrate the bloodstream and cause inflammation. This inflammation can contribute to the development of cardiovascular diseases such as heart attacks, strokes, high blood pressure, and arrhythmias.
- Allergies and Irritation: Air pollution can trigger allergic reactions and irritate the eyes, nose, and throat. It can worsen symptoms for individuals with allergies, hay fever, and other respiratory conditions.
- Impaired Lung Development: Children exposed to air pollution may experience impaired lung development, leading to reduced lung function and respiratory problems throughout their lives.
- Increased Mortality: Long-term exposure to high levels of air pollution has been linked to increased mortality rates, primarily due to respiratory and cardiovascular diseases.
- Mental Health Effects: While the physical health impacts of air pollution are well-documented, recent studies suggest a connection between air pollution and mental health issues. Exposure to air pollution has been associated with an increased risk of depression, anxiety, cognitive decline, and neurodevelopmental disorders in children.
Air Pollution Can Cause Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer for both men and women and while it is well known that smoking is the number one cause of lung cancer, air pollution is also a cause. Overwhelming evidence has shown that particle pollution in our air can cause cancer; air particle pollutants come from vehicle exhaust, coal-fired power plants, and many other industrial sources. Particle pollution is known to increase the risk of dying early, heart disease, and asthma attacks, and can interfere with the healthy growth and functioning of the lungs.
Particle pollution is the tiny solid and liquid particles in the air that are made up of various components, including acids, organic chemicals, metals, soil, and dust particles. Sources include wood stoves, forest fires, vehicles, manufacturing plants, factories, and power plants. The particles themselves are microscopic, much smaller than the diameter of a human hair and smaller than a grain of sand.
Bigger particles can irritate your eyes, nose, and throat, but our natural bodily defenses counteract this by coughing or sneezing them out. Unfortunately, these defense mechanisms do not work on smaller particles that get trapped in your lungs and can even make their way into your bloodstream.
It’s important to note that the severity of health effects depends on the concentration and duration of exposure to pollutants. Individuals with pre-existing health conditions, the elderly, and children are generally more vulnerable to the harmful effects of air pollution.
While many other countries have far worse air quality and air pollution problems, the United States is not immune. Medical research has proven that what we cannot see can still hurt us.
According to Dr. Norman Edelman, MD, Senior Scientific Advisor to the American Lung Association, “We know that fine particles can enter deep into the lungs and are linked to lung cancer, and even more research needs to be done on the precise way that these particles start the cancerous process within the lungs.” He continues to say, “Anyone who lives where particle pollution levels are high is at risk. Some people face higher risk, including children, the elderly, people with lung and heart disease and diabetes, people with low incomes, and people who work or exercise outdoors.”
Next Steps
There are things you can do to ensure you aren’t exposing yourself or your loved ones to unnecessary air pollution.
- Check the air quality index
- Avoid exercising along heavily traveled highways or near industrial areas
- Don’t burn wood or trash
- Don’t idle vehicles, especially diesel engines
- Use air purifiers indoors
- Avoid exposure to polluted areas
To help mitigate the health risks associated with air pollution, it is crucial to reduce emissions at their sources, improve air quality regulations and promote clean energy alternatives. You can also call on Congress to protect the Clean Air Act, the law responsible for the nation’s progress to clean up particle pollution.
The city of Chicago has also tried to address air pollution in Chicago. The city has implemented various initiatives in the aforementioned Air Quality Ordinance to reduce emissions and improve air quality. The city has implemented stricter vehicle emission standards and is promoting public transportation and encouraging renewable energy sources. Additionally, community organizations and advocacy groups are working to raise awareness about the impact of air pollution and push for policies that prioritize environmental justice.
A Compassionate Advocate Is Here for You
The team at Vogelzang Law is here to listen and provide the support you need. We are committed to holding negligent corporations accountable and being the fierce advocates you and your family deserve.
Contact us today at (312) 466-1669 or through our online form for a free, no-obligation consultation to discuss your situation. Let us be your safe harbor and help you take the first step toward finding answers.